MiCA Grandfathering Deadlines Are Ending — and DORA Compliance Becomes Mandatory
Most MiCA transitional (“grandfathering”) periods for former VASPs expire by the end of 2025, with a limited number extending to June 2026.
After that, firms generally need a CASP authorisation under MiCA — and must be ready for DORA compliance as part of operating as a regulated entity.
As the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) enters its final implementation phase, one critical topic is often underestimated: the end of national grandfathering (transitional) periods for former VASPs.
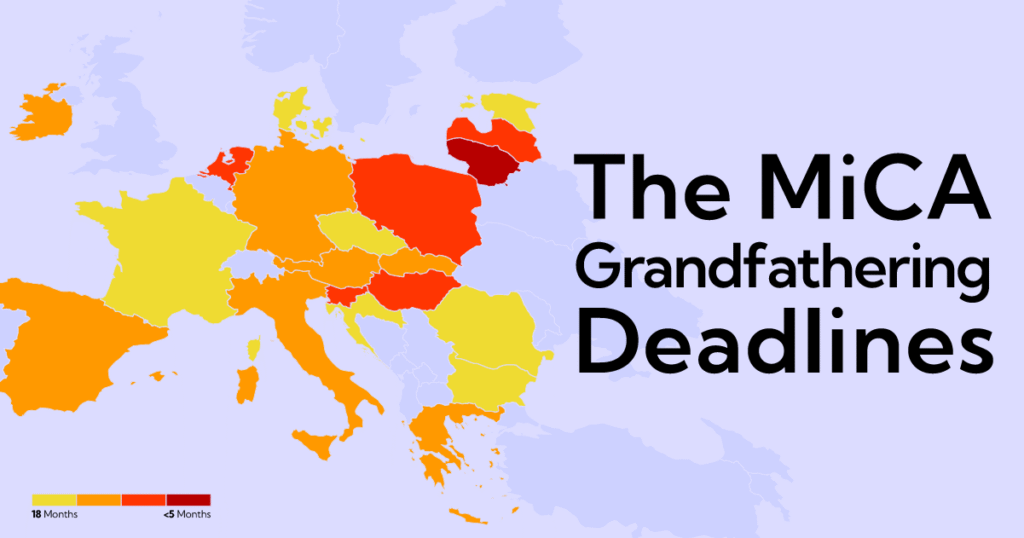
According to ESMA’s official list published under Article 143(3) MiCA, most EU and EEA Member States will see their transitional regimes expire by the end of 2025, with only a limited number allowing operation until mid-2026. After these dates, operating under a former VASP regime will no longer be sufficient.
Importantly, obtaining a CASP authorisation under MiCA does not only introduce licensing and conduct requirements. It also brings a second regulatory layer: compliance with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA). In practice, MiCA compliance without DORA readiness is no longer a viable regulatory strategy.
What Is the MiCA Grandfathering (Transitional) Regime?
MiCA’s grandfathering regime was introduced to allow certain crypto-asset service providers that were legally operating under national law before MiCA to continue their activities temporarily. This transitional period was designed as a time-limited bridge — not a permanent exemption.
Each Member State was allowed to determine the length of this transitional period and notify ESMA of its decision. As a result, deadlines differ by country, but the regulatory outcome is the same across the EU and EEA.
Below is a simplified summary of the transitional periods based on ESMA’s official list under Article 143(3). Exact end dates should always be confirmed with national regulators.
| Transitional period length | Typical deadline (country-dependent) | Member States |
|---|---|---|
| 18 months | Often until around June 2026 | France; Czechia; Denmark; Estonia; Cyprus; Malta; Luxembourg; Bulgaria; Croatia; Romania |
| 12 months | Often until around end of 2025 | Germany; Ireland; Greece; Spain; Italy; Austria; Slovakia |
| 6 months | Often until around mid-2025 | Latvia; Netherlands; Poland; Hungary; Slovenia |
| Short (~5 months) | Early 2025 | Lithuania |
| TBA / Not listed | Not specified in the ESMA list at the time of publication | Belgium; Portugal; Norway (EEA) |
Source:
ESMA
Next Step: Assess Your DORA Readiness